Edvancer's Knowledge Hub
5 use cases to get you started with data science

In the past decade, we’ve been witness to an immense data explosion. With most information being shared digitally, and more still being stored on cloud, almost every industry is sitting on a treasure trove of data. If mined properly, this data can reveal information on customer preferences, tastes, usage in real-time, and much more.
However, most organizations still don’t know how to use up to 80% of their data, since most data exists in an unstructured format.
The key question is how to use your imagination to pick what data to correlate and analyse. Here are some use cases to get you started on what to structure your data for, and how:
 2. Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis (also known as opinion mining) refers to the use of natural language processing, text analysis and computational linguistics to identify and extract subjective information in source materials.
Using sentiment analysis techniques, companies can respond to negative (or positive) brand perception.
When a company releases a new product, monitoring and analyzing social media content can play a large role in quickly remediating bugs and errors.
PR for political figures and celebrities depends heavily on sentiment analysis and how the person is perceived by people on social media.
Here is a good example of how sentiment analysis is used to mine social data.
2. Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis (also known as opinion mining) refers to the use of natural language processing, text analysis and computational linguistics to identify and extract subjective information in source materials.
Using sentiment analysis techniques, companies can respond to negative (or positive) brand perception.
When a company releases a new product, monitoring and analyzing social media content can play a large role in quickly remediating bugs and errors.
PR for political figures and celebrities depends heavily on sentiment analysis and how the person is perceived by people on social media.
Here is a good example of how sentiment analysis is used to mine social data.
 3. Clickstream analysis
Clickstream data is the trail of digital breadcrumbs left by users as they click their way through a website, and it’s loaded with valuable customer information for businesses.
Clickstream analysis is the process of collecting, analyzing, and reporting aggregate data about which pages visitors visit, and in what order. This reveals usage patterns, which in turn gives a heightened understanding of customer behaviour. This use of the analysis creates a user profile that aids in understanding the types of people that visit a company’s website.
3. Clickstream analysis
Clickstream data is the trail of digital breadcrumbs left by users as they click their way through a website, and it’s loaded with valuable customer information for businesses.
Clickstream analysis is the process of collecting, analyzing, and reporting aggregate data about which pages visitors visit, and in what order. This reveals usage patterns, which in turn gives a heightened understanding of customer behaviour. This use of the analysis creates a user profile that aids in understanding the types of people that visit a company’s website.
 Source: Internet search engine marketing.
Google Analytics is the most commonly used clickstream analytics platform, which provides insights into where visitors come from, how long they stay, conversion rates and more.
4. Fraud Detection
Fraud is a billion-dollar business on the rise. Nearly 30% of companies worldwide have reported being victims of fraud in the past year.
We know that financial institutions monitor our spending habits on a real-time basis. In addition to the transaction records for authorization and approvals, banks and credit card companies collect a lot more information from location, your life style, your tastes, income, account balances and employment details, and credit history and transaction history.
Traditional methods of data analysis have long been used to detect fraud. Fraud instances can be similar in content and appearance but rarely are identical. Hence, data companies have to constantly update themselves with the new techniques of fraud detection. One early example of successful implementation of data analysis techniques in the banking industry is the FICO, Falcon fraud assessment system.
Source: Internet search engine marketing.
Google Analytics is the most commonly used clickstream analytics platform, which provides insights into where visitors come from, how long they stay, conversion rates and more.
4. Fraud Detection
Fraud is a billion-dollar business on the rise. Nearly 30% of companies worldwide have reported being victims of fraud in the past year.
We know that financial institutions monitor our spending habits on a real-time basis. In addition to the transaction records for authorization and approvals, banks and credit card companies collect a lot more information from location, your life style, your tastes, income, account balances and employment details, and credit history and transaction history.
Traditional methods of data analysis have long been used to detect fraud. Fraud instances can be similar in content and appearance but rarely are identical. Hence, data companies have to constantly update themselves with the new techniques of fraud detection. One early example of successful implementation of data analysis techniques in the banking industry is the FICO, Falcon fraud assessment system.
 5. Customer Loyalty Program Analytics
Today, customers are more informed, they have more options, and they have higher expectations, and so, retaining current customers has become a high priority. Loyalty programs have sprung up in every consumer-related industry, from retail to restaurants, cruise lines to charge cards.
But if loyalty programs are now the norm, simply having the program isn’t enough to differentiate a company from its competitors. Hence, customers begin to expect discounts and deals. They soon learn to wait for sales and specials, and their membership cards become a means for price-shopping rather than increasing their loyalty.
The companies with strong loyalty programs rely on customer analytics to drive their strategies and create measurable business impact.
Starbucks saw dollars loaded on Starbucks Cards surge to a record $1.6 billion in its Q1 Fiscal 2015, up 17% over prior year Q1. The company now has over 9 million total members.
For me, the 5 categories I have outlined here represent the areas in which data science is applied the most. Of course, there are so many other applications of data science and there will be many new categories as the tools become more widespread.
5. Customer Loyalty Program Analytics
Today, customers are more informed, they have more options, and they have higher expectations, and so, retaining current customers has become a high priority. Loyalty programs have sprung up in every consumer-related industry, from retail to restaurants, cruise lines to charge cards.
But if loyalty programs are now the norm, simply having the program isn’t enough to differentiate a company from its competitors. Hence, customers begin to expect discounts and deals. They soon learn to wait for sales and specials, and their membership cards become a means for price-shopping rather than increasing their loyalty.
The companies with strong loyalty programs rely on customer analytics to drive their strategies and create measurable business impact.
Starbucks saw dollars loaded on Starbucks Cards surge to a record $1.6 billion in its Q1 Fiscal 2015, up 17% over prior year Q1. The company now has over 9 million total members.
For me, the 5 categories I have outlined here represent the areas in which data science is applied the most. Of course, there are so many other applications of data science and there will be many new categories as the tools become more widespread.
Share this on





Follow us on




- Real-Time Analytics
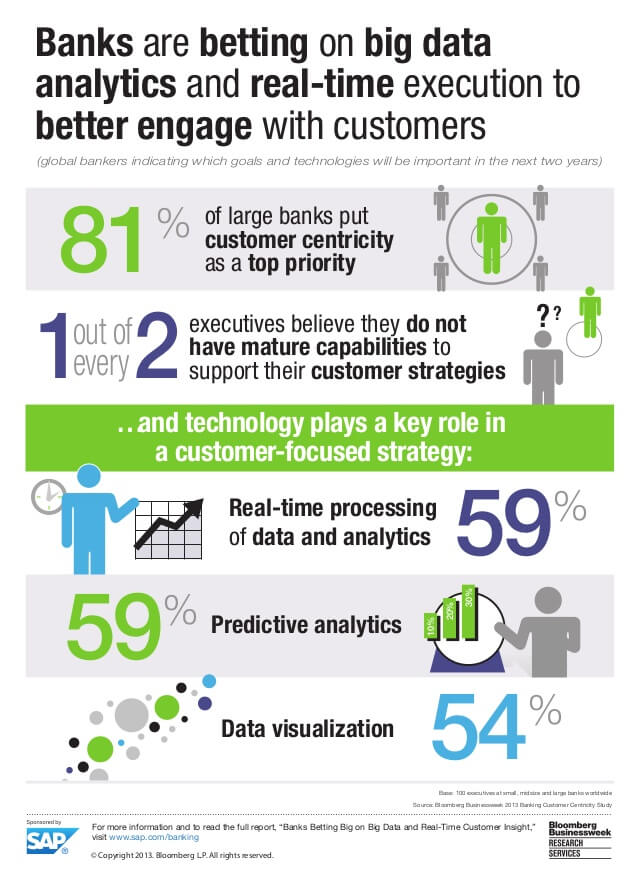 2. Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis (also known as opinion mining) refers to the use of natural language processing, text analysis and computational linguistics to identify and extract subjective information in source materials.
Using sentiment analysis techniques, companies can respond to negative (or positive) brand perception.
When a company releases a new product, monitoring and analyzing social media content can play a large role in quickly remediating bugs and errors.
PR for political figures and celebrities depends heavily on sentiment analysis and how the person is perceived by people on social media.
Here is a good example of how sentiment analysis is used to mine social data.
2. Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis (also known as opinion mining) refers to the use of natural language processing, text analysis and computational linguistics to identify and extract subjective information in source materials.
Using sentiment analysis techniques, companies can respond to negative (or positive) brand perception.
When a company releases a new product, monitoring and analyzing social media content can play a large role in quickly remediating bugs and errors.
PR for political figures and celebrities depends heavily on sentiment analysis and how the person is perceived by people on social media.
Here is a good example of how sentiment analysis is used to mine social data.
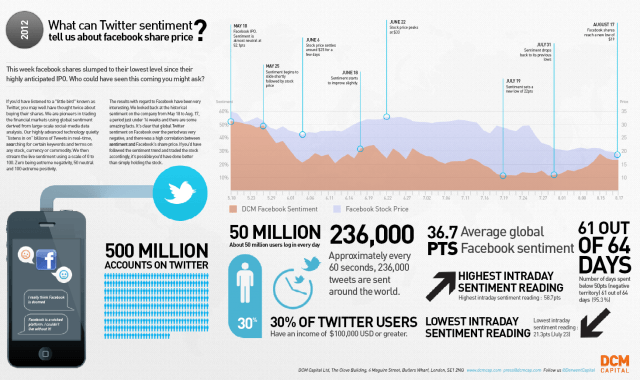 3. Clickstream analysis
Clickstream data is the trail of digital breadcrumbs left by users as they click their way through a website, and it’s loaded with valuable customer information for businesses.
Clickstream analysis is the process of collecting, analyzing, and reporting aggregate data about which pages visitors visit, and in what order. This reveals usage patterns, which in turn gives a heightened understanding of customer behaviour. This use of the analysis creates a user profile that aids in understanding the types of people that visit a company’s website.
3. Clickstream analysis
Clickstream data is the trail of digital breadcrumbs left by users as they click their way through a website, and it’s loaded with valuable customer information for businesses.
Clickstream analysis is the process of collecting, analyzing, and reporting aggregate data about which pages visitors visit, and in what order. This reveals usage patterns, which in turn gives a heightened understanding of customer behaviour. This use of the analysis creates a user profile that aids in understanding the types of people that visit a company’s website.
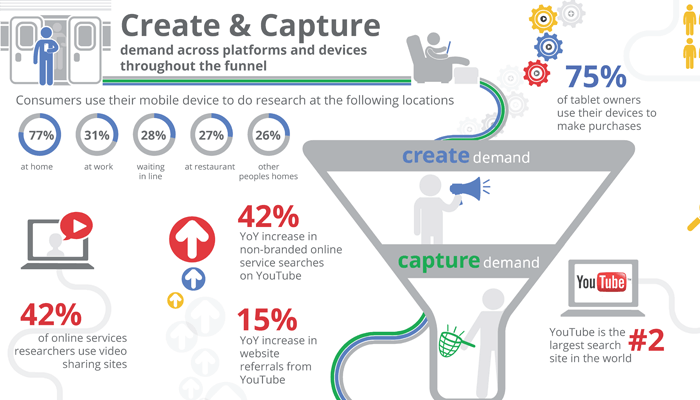 Source: Internet search engine marketing.
Google Analytics is the most commonly used clickstream analytics platform, which provides insights into where visitors come from, how long they stay, conversion rates and more.
4. Fraud Detection
Fraud is a billion-dollar business on the rise. Nearly 30% of companies worldwide have reported being victims of fraud in the past year.
We know that financial institutions monitor our spending habits on a real-time basis. In addition to the transaction records for authorization and approvals, banks and credit card companies collect a lot more information from location, your life style, your tastes, income, account balances and employment details, and credit history and transaction history.
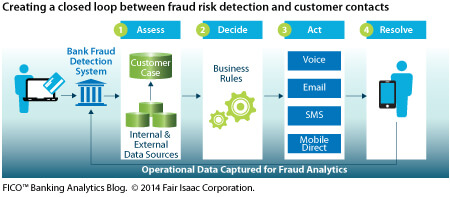
Traditional methods of data analysis have long been used to detect fraud. Fraud instances can be similar in content and appearance but rarely are identical. Hence, data companies have to constantly update themselves with the new techniques of fraud detection. One early example of successful implementation of data analysis techniques in the banking industry is the FICO, Falcon fraud assessment system.
Source: Internet search engine marketing.
Google Analytics is the most commonly used clickstream analytics platform, which provides insights into where visitors come from, how long they stay, conversion rates and more.
4. Fraud Detection
Fraud is a billion-dollar business on the rise. Nearly 30% of companies worldwide have reported being victims of fraud in the past year.
We know that financial institutions monitor our spending habits on a real-time basis. In addition to the transaction records for authorization and approvals, banks and credit card companies collect a lot more information from location, your life style, your tastes, income, account balances and employment details, and credit history and transaction history.
Traditional methods of data analysis have long been used to detect fraud. Fraud instances can be similar in content and appearance but rarely are identical. Hence, data companies have to constantly update themselves with the new techniques of fraud detection. One early example of successful implementation of data analysis techniques in the banking industry is the FICO, Falcon fraud assessment system.
 5. Customer Loyalty Program Analytics
Today, customers are more informed, they have more options, and they have higher expectations, and so, retaining current customers has become a high priority. Loyalty programs have sprung up in every consumer-related industry, from retail to restaurants, cruise lines to charge cards.
But if loyalty programs are now the norm, simply having the program isn’t enough to differentiate a company from its competitors. Hence, customers begin to expect discounts and deals. They soon learn to wait for sales and specials, and their membership cards become a means for price-shopping rather than increasing their loyalty.
The companies with strong loyalty programs rely on customer analytics to drive their strategies and create measurable business impact.
Starbucks saw dollars loaded on Starbucks Cards surge to a record $1.6 billion in its Q1 Fiscal 2015, up 17% over prior year Q1. The company now has over 9 million total members.
For me, the 5 categories I have outlined here represent the areas in which data science is applied the most. Of course, there are so many other applications of data science and there will be many new categories as the tools become more widespread.
5. Customer Loyalty Program Analytics
Today, customers are more informed, they have more options, and they have higher expectations, and so, retaining current customers has become a high priority. Loyalty programs have sprung up in every consumer-related industry, from retail to restaurants, cruise lines to charge cards.
But if loyalty programs are now the norm, simply having the program isn’t enough to differentiate a company from its competitors. Hence, customers begin to expect discounts and deals. They soon learn to wait for sales and specials, and their membership cards become a means for price-shopping rather than increasing their loyalty.
The companies with strong loyalty programs rely on customer analytics to drive their strategies and create measurable business impact.
Starbucks saw dollars loaded on Starbucks Cards surge to a record $1.6 billion in its Q1 Fiscal 2015, up 17% over prior year Q1. The company now has over 9 million total members.
For me, the 5 categories I have outlined here represent the areas in which data science is applied the most. Of course, there are so many other applications of data science and there will be many new categories as the tools become more widespread.
Manu Jeevan
Manu Jeevan is a self-taught data scientist and loves to explain data science concepts in simple terms. You can connect with him on LinkedIn, or email him at manu@bigdataexaminer.com.
Latest posts by Manu Jeevan (see all)
- Python IDEs for Data Science: Top 5 - January 19, 2019
- The 5 exciting machine learning, data science and big data trends for 2019 - January 19, 2019
- A/B Testing Made Simple – Part 2 - October 30, 2018
Follow us on
Free Data Science & AI Starter Course

